Event Trigger System

The Schema-Aware Trigger System in SkyrimNet allows you to define custom reactions to in-game events. This system makes NPCs, the player character, and the world itself more dynamic, offering immersive responses that feel tailored to what's happening in real time.
Triggers are event-driven rules that check for specific gameplay conditions, such as casting a spell or using an item. When conditions are met, a templated response is generated — from a whispered thought to a loud reaction from nearby NPCs. Triggers can:
- React to spells, items, combat, dialogue, animations, and more
- Generate narrative text or dialogue
- Silently record events for memory or future logic
- Update persistent character data
Triggers, for now, dont allow using additional scripts or decorators on their descriptions.
How Triggers Work
Each trigger consists of:
- Event Type: The in-game action that activates the trigger (e.g.,
spell_cast) - Conditions: Fields like spell name, editor ID, or actor type that filter the trigger
- Response Content: A written message, using variables and templates
- Response Type: Defines how the line is delivered (thought, speech, narration)
- Audience: Who hears or sees the response (player, NPCs, etc.)
- Optional Metadata: Priority, probability, and cooldown timers
Triggers can be created manually or automatically based on spell/item customizations.
Trigger Lifecycle
-
Event Occurs
(e.g. spell cast, item equipped, animation played) -
Schema Validation
Event data is validated against its registered schema. -
Condition Evaluation
All trigger conditions must match. -
Probability Check
Trigger may randomly fire based on configured chance. -
Cooldown Check
Prevents repeated firing. -
Response Execution
Response content is rendered and executed
🎭 Response Types
Each response style sets a different narrative tone and use case.
Response Types
| Response Type | Description | Visibility / Effect | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🧠 Player Thought | Internal monologue shown to the player | Player only, no NPC awareness | Sensations, instincts, reflections |
| 🗣️ Player Dialogue | Spoken by the player character | Heard by selected audience; can affect NPC reactions and memories | Auto-comments, taunts, reactive speech |
| 📖 Direct Narration | Third-person or narrator-style description | Not attributed to player or NPC speech | Combat descriptions, atmosphere, cinematic or adult scenes |
| 🕒 Persistent Event (No Response) | Records the event without visible output | Affects memory, emotions, or future triggers | Hidden consequences, long-term logic |
| 📓 Create Diary Entry | Writes a persistent diary entry | Stored and readable later | Quest logs, major story moments, personal memories |
| 🧬 Update Dynamic Bio | Updates NPC biography/personality state | Alters future LLM context, dialogue, and behavior | Relationship changes, corruption arcs, character growth |
👥 Audience Options
You can target who receives the trigger response:
| Audience | Description |
|---|---|
player | Only the player sees/hears the response |
originator | The actor who caused the event (e.g. spell caster) |
target | The actor the event is aimed at (e.g. spell recipient) |
nearby | All nearby actors (within a set distance) |
npcs | All nearby NPCs (excludes the player) |
everyone | Player and all nearby NPCs |
This allows you to control perspective and immersion for every response.
🎯 Conditions and Events
Each trigger uses schema-aware conditions tailored to its event type. For example, a spell_cast event includes:
spell: The display name of the spell (e.g., Ironflesh)spell_editor_id: The internal ID of the spellactor: The caster of the spell
These fields can be matched using operators like equals, contains, or starts_with.
🧾 Response Templating
Response text is written using a flexible template language with variable support. You can insert values dynamically:
Templates allow you to reuse trigger logic across characters and situations without hardcoding dialogue.
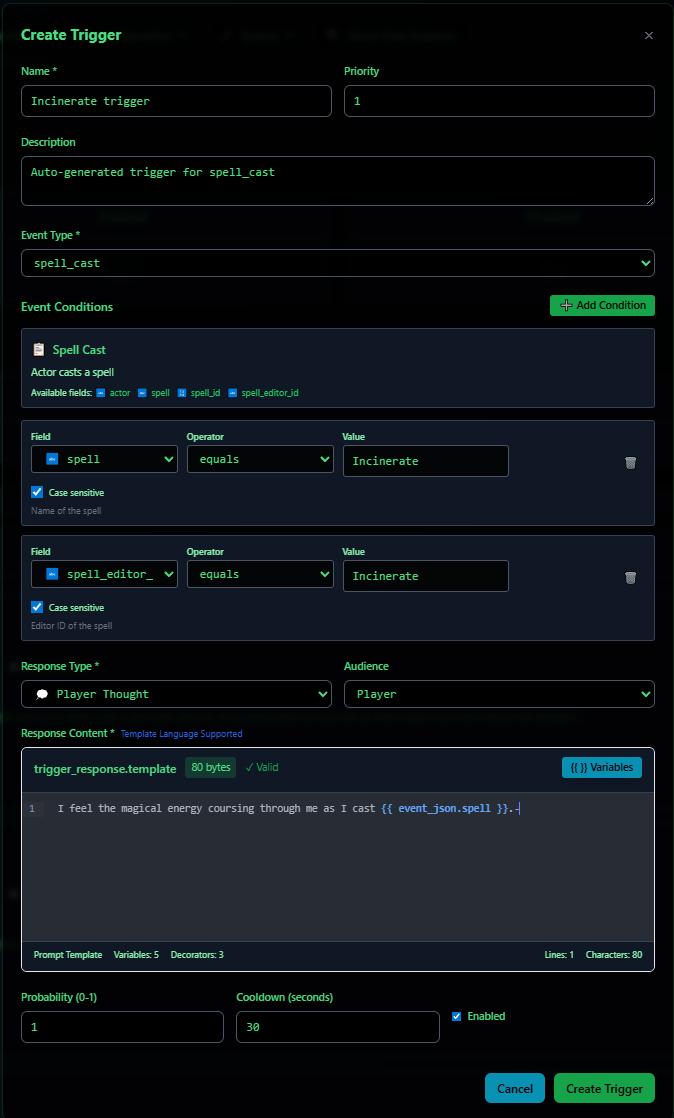
🧪 Example: Ironflesh Spell Reaction
Trigger Name: Ironflesh Trigger
Event: spell_cast
Conditions:
spell equals Ironfleshspell_editor_id equals Ironflesh
Response Type: Player Thought
Audience: Player
Cooldown: 30 seconds
Response:
I feel my skin tingle as it hardens while I cast {{ event_json.spell }}.
🔧 Managing Triggers
Triggers are created and edited via the Trigger Management UI. Each trigger supports:
- Setting priority (used when multiple triggers match)
- Configuring chance (e.g., 100% reliable or random 25% chance)
- Defining cooldown to prevent repeated responses
- Live enabling/disabling without restarting the game
You can also search, filter, and reload triggers instantly. The UI is schema-driven and adapts to the selected event type for easier configuration.
For triggers to be listed properly in the web-ui, make sure their yaml file name matches exactly with the trigger name, contained in his own setting.
Quick Trigger Creation
You can use the "create trigger" button associated with items and spells you browse on the Game data explorer.
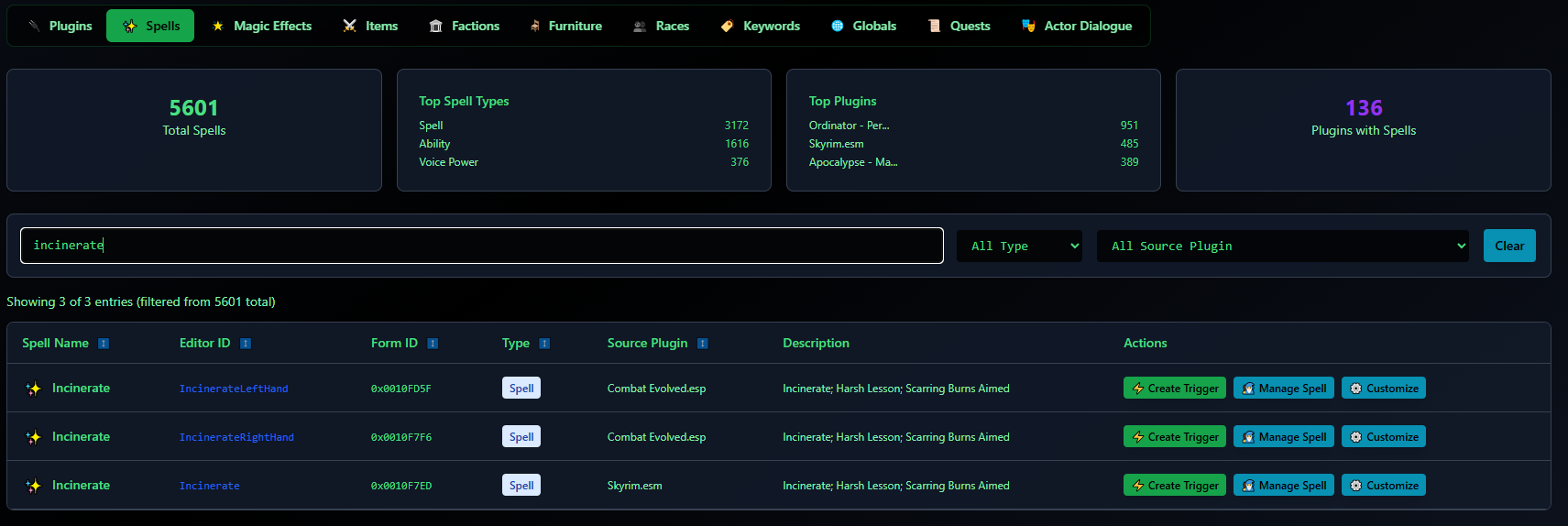
The system will then take you to a fully pregenerated trigger, containing all relevant variables to that event. You can then edit it at your leisure, like changing the title, response types, description, etc.
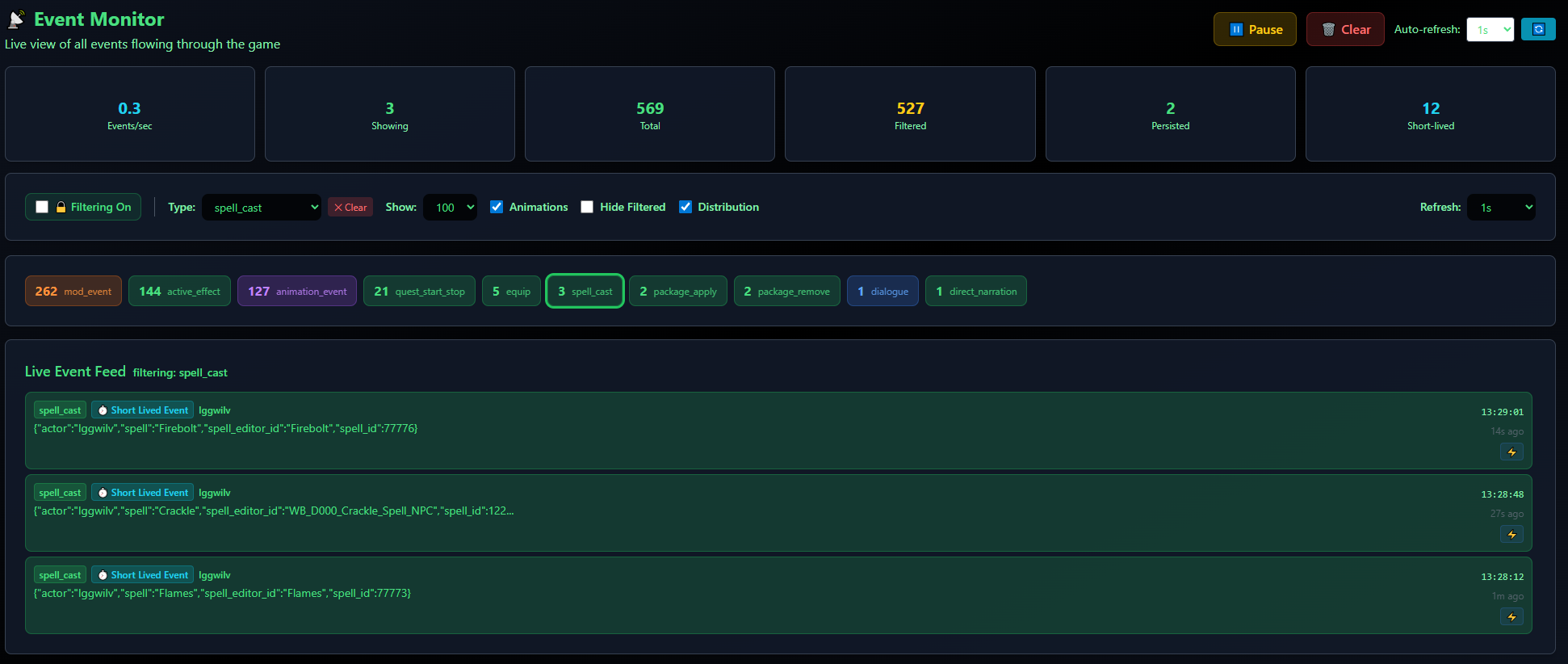
The Event Monitor also includes a "create trigger button". This allows you to use generate pre-made templates for all kinds of events, as they flow in your game , in real time.
🔄 Integration with Other Systems
Triggers integrate seamlessly with:
- Memory and Emotion Systems: Feeding into emotional state and memory entries
- NPC Dialogue and Ambient Behavior: Creating realistic chatter or commentary in response to events
This makes the trigger system a bridge between world simulation and narrative design — powerful for both modders and storytellers.